It is a type of positive carry collar that is constructed by simultaneously purchasing and selling of out of the money calls and puts with the strike prices of which creating a band encircled by an upper and lower bound.
Interest rate cap floor and collar.
Table 3 interest rate collar example.
Associated bank offers interest rate swaps structured with collars.
The issuer of a floating rate note might use this to cap the upside of his debt service and pay for the cap with a floor.
This organization has purchased a 5 cap and sold a 2 floor which provides the organization with an interest rate collar of 2 to 5.
If the benchmark rate exceeds the cap associated bank pays you the difference for the period.
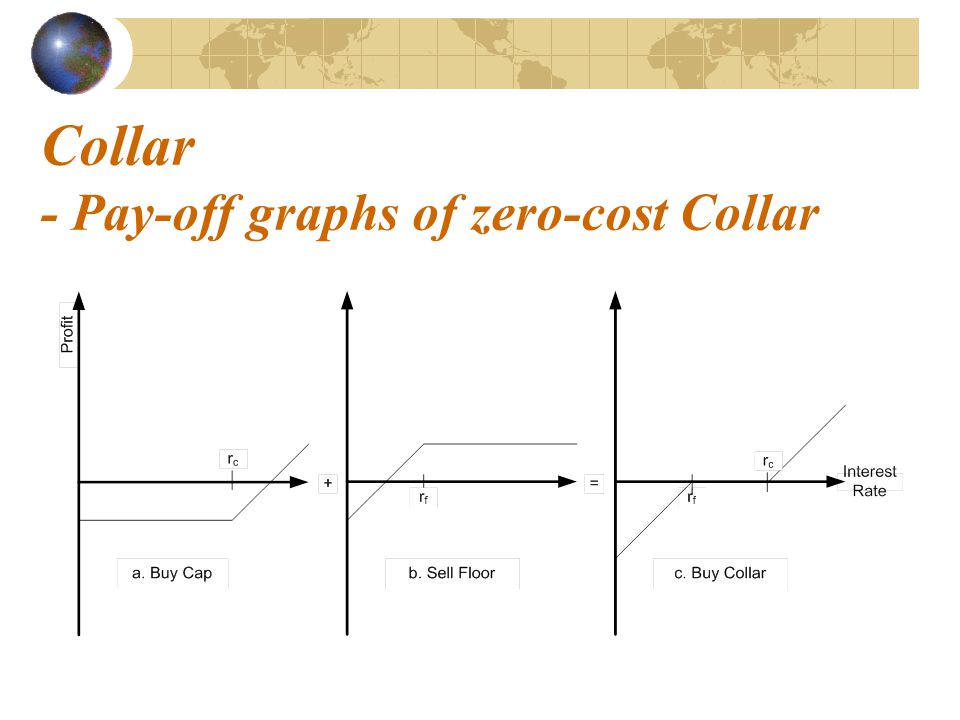
It protects a borrower against rising rates and establishes a floor on declining rates through the purchase of an interest rate cap and the simultaneous sale of an interest rate floor.
The call and put options take on the role of caps and floors.
As seen from the table borrower is already reducing its premium costs to 100 000 80 000 20 000 buy selling floor and also limiting its interest costs at 5 when interest rate rises above the cap level.
Interest rate swap in hedging variable rate debt with a swap an organization agrees to pay out a fixed amount each month to a counterparty in exchange for receipt of a variable rate.
The premium for an interest rate collar also depends on the rollover frequency and how you make your premium payments.
An interest rate collar is an option used to hedge exposure to interest rate moves.
Typically the premium of the cap is designed to exactly match that of the.
Indeed its interest rate delta is negative.
Imagine buying a 1 70 libor cap and selling a 1 70 floor.
A collar involves selling a covered call and simultaneously buying a protective put with the same expiration establishing a floor and a cap on interest rates.
Work with associated bank to determine your preferred interest rate range marked by a cap and a floor.
As stated before a collar establishes a defined range floor and cap of interest rates the hedger is subjected to as opposed to a single fixed swap rate.
Caps floors and collars 13 interest rate collars a collar is a long position in a cap and a short position in a floor.
We compare each period s interest rate to a benchmark rate typically libor.
Caps floors and collars 8 interest rate sensitivity of a cap the cap pays off when interest rates go up.
Therefore it is a bearish position in the bond market.
While the collar effectively hedges.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/strategy-4086857_19201-23485cf7c4bf4dbbb95c93f267285f16.jpg)